Root Cause Analysis: Meaning, Tools, Pitfalls and More
15 Jun, 2022
A Root Cause Analysis is a method of problem-solving that is used to identify the root causes of issues or problems. By identifying and addressing the root causes, organizations can prevent these issues from happening again. In this blog post, we will explore every aspect of Root Cause Analysis. We discuss the meaning, when to use it, who can use it, its goals, different tools, its benefits and its pitfalls. As well as software to help you overcome these pitfalls.
What is Root Cause Analysis?
Root Cause Analysis refers to the process of studying and understanding the root cause of the problem that leads to non-conformances in the organization. It involves broader investigations by analyzing every piece of detail crucial for the implementation of corrective actions. The organization can also base on the information derived from Root Cause Analysis to bulletproof its workflows from being affected by the reoccurrence of the same problem in the future. To achieve this, a series of steps could be adopted and implemented.
When should you use a Root Cause Analysis?
Root Cause Analysis can help to fix problems, but it can also be used to improve processes, prevent quality issues, and prevent problems from happening in the first place. In general, when a problem is found or a requirement is not met, first you will create a Non-Conformance Report, and then the appointed party will do a Root Cause Analysis.
Situations, which can result in a Root Cause Analysis are:
- A process is not meeting its quality or requirement goals
- There are too many defects in a process
- Customer complaints are increasing
- There is a sudden drop in productivity
Root Cause Analysis can be used in many different types of industries such as space, aerospace, defence, manufacturing, healthcare, service, and construction.
Who can do a Root Cause Analysis?
Basically, the organization can choose to employ both internal and external teams of experts to investigate the problem. But this could also depend on the scale of the problem and how much impact it caused on the organization. If there is an occurrence of a major non-conformance, a sophisticated team of experts has to get involved to broadly analyze the problem.
External players could also be involved in the process of executing the Root Cause Analysis to gather high-quality findings from an independent perspective, which the organization may badly need to make proper decisions.
The goal of a Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis is primarily implemented to achieve 3 major goals. And these include the following:
- Identifying the root cause of the problem. Understanding why non-conformance occurred in the organization is always the first priority when implementing or running Root Cause Analysis. Without identifying why problems or non-conformances occurred, everything that follows become meaningless. However, when the problem is identified, it helps in the appropriate execution of strategic interventions in form of corrective and preventive actions
- Deriving the best way to fix the problem. Identifying the problem is not enough without understanding the right and appropriate fixes required. This second goal of the Root Cause Analysis is also important in the sense that the right solutions are adopted in response to the problem that has been identified. It takes the right approach to fix or handle non-conformances in the organization. When there are failures or weaknesses in the entire process, the core goals and objectives could be considered useless. So, handling non-conformances could involve a series of measures, steps and recommendations that could be employed to deal with the problem.
- Drawing important conclusions and learning critical lessons. After understanding what caused non-conformance in the organization, it becomes a stepping stone in drawing important conclusions and even learning crucial lessons that help the organization bulletproof itself from similar occurrences in the future.
Tools to identify problems and analyse data
There are different types of analysis to get to the root cause of a problem. In this way, Root Cause Analysis is seen as a bundle of different tools and methodologies. And the type of analysis used usually depends on the problem being solved, as well as the industry or sector in which an organization operates.
Here are some popular Root Cause Analysis tools:
5 Why Analysis
This is a simple yet effective tool for getting to the root cause of a problem. As the name suggests, 5 Why Analysis requires the problem solvers to ask the question “why” five times. Doing this helps to peel back the layers of a problem until its root cause is uncovered.
The 5 Why Analysis tool is especially useful for simple problems that have a linear cause and effect. It’s also quite popular because it’s easy to use and doesn’t require too much data.
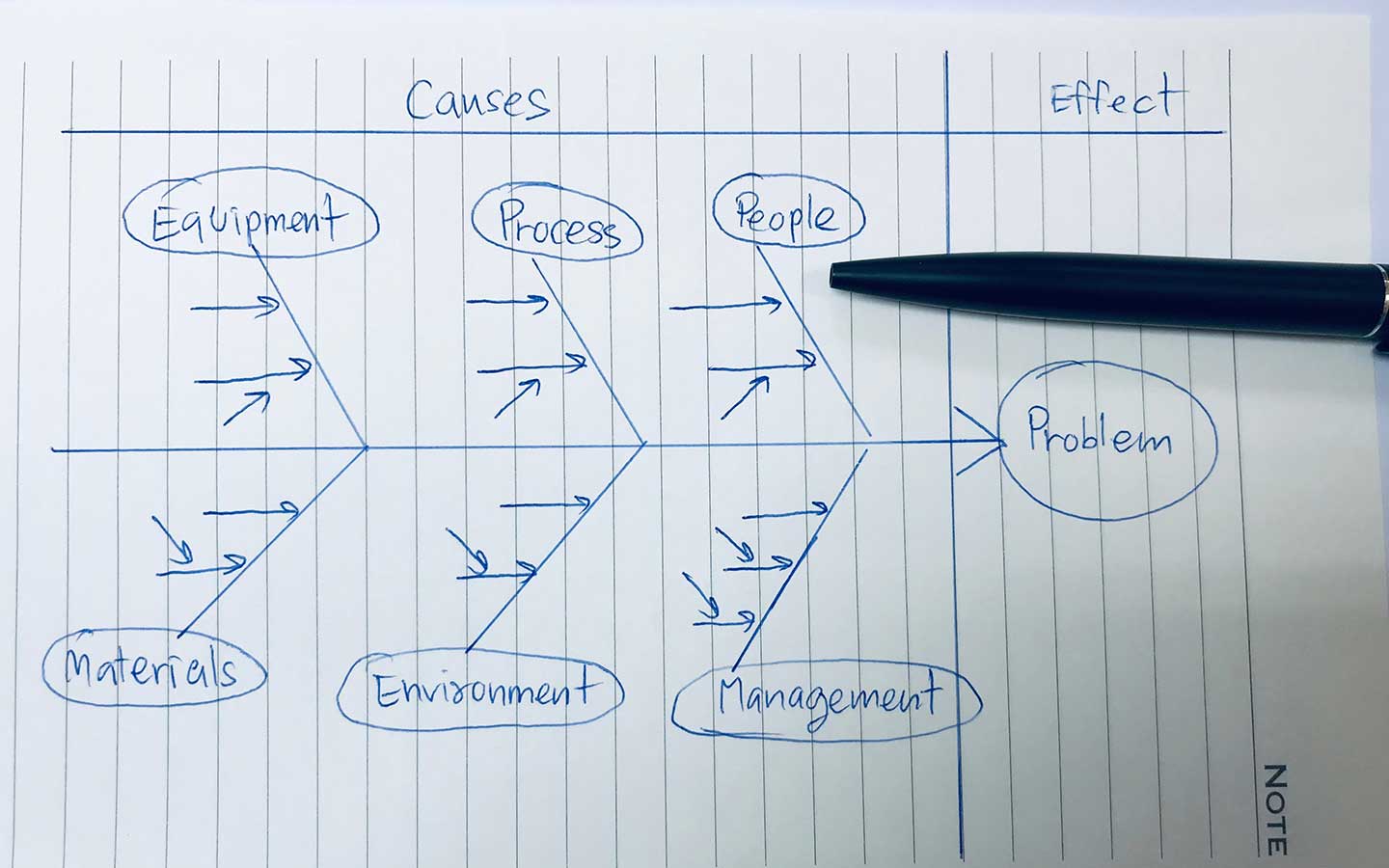
Ishikawa Diagram
This tool is also popularly used in different industries for Root Cause Analysis. It is also known as a fishbone diagram or cause and effect diagram. The Ishikawa Diagram helps problem solvers to visually display the different possible causes of a problem. In this way, it becomes easier to identify the root cause. Steps in using an Ishikawa Diagram include the following:
- Identify the problem.
- Draw an arrow with the problem at the end.
- Draw lines coming out from the arrow with the categories people, machines, materials, methods, environment, and measurements.
After analysing you will find the potential causes.
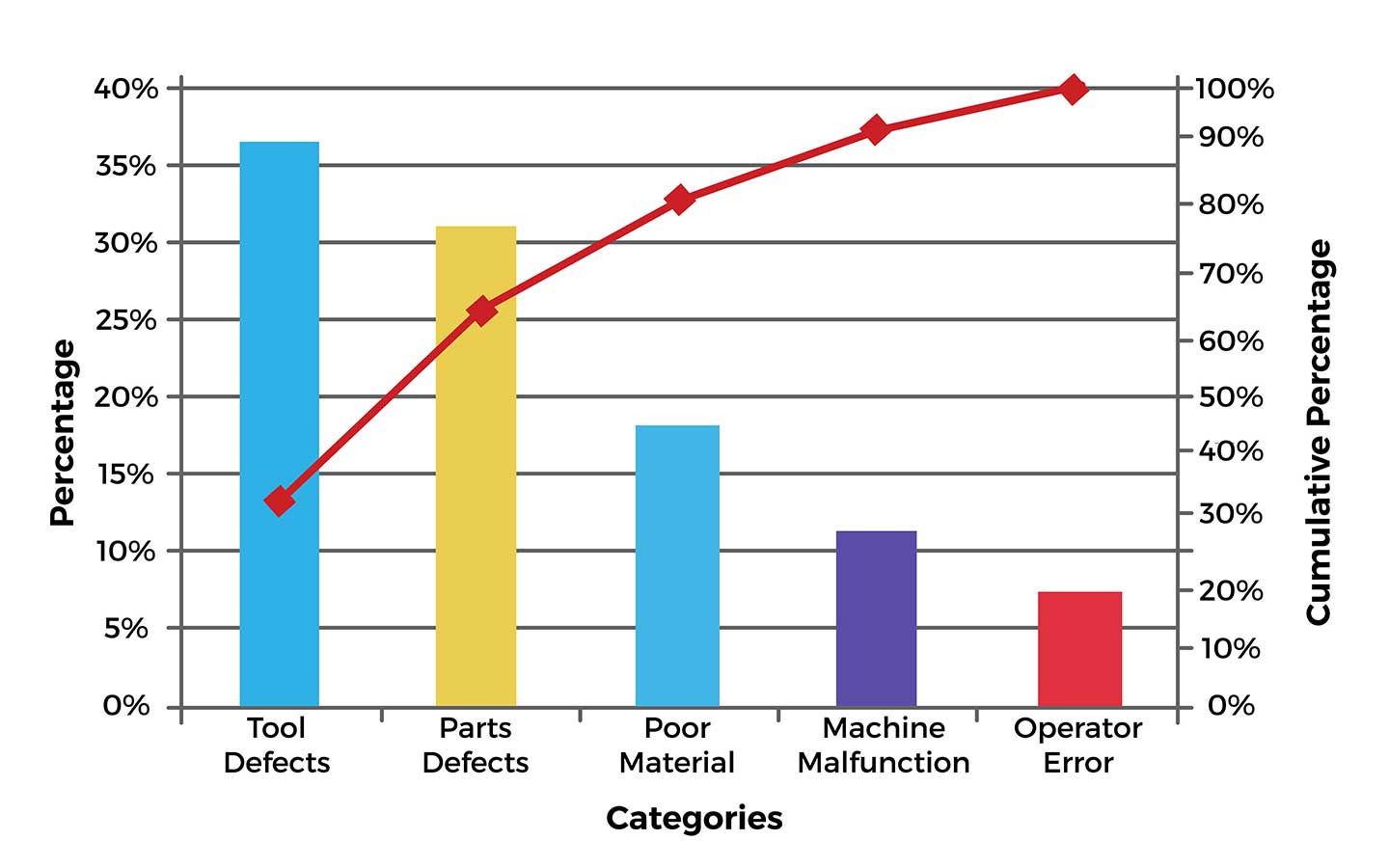
Pareto Chart (The 80/20 Rule)
This is a graphical tool used for prioritization. Pareto Chart is popular in different industries as it helps organizations quickly identify which areas require immediate attention. It also allows decision-makers to see which problems are more important than others.
In using a Pareto Chart, the first step is to determine the different factors that contribute to the problem. Then, these factors are ranked according to their contribution or impact on the problem. After which, a graphical representation is made to easily see which areas need more attention.
The Pareto chart is based on the principle that states that 80% of the effects come from 20% of the causes. In other words, a small number of factors contribute to the majority of the problems. Fixing this 20% can have a big impact on the entire system.
The Benefits of Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis offers significant benefits to the organization and these include;
Preparing for the worst and mitigating the effects
The organization is able to understand in detail what, who, where and when the problem of non-conformance has happened. With a better understanding of the problem, it helps to devise the right strategies and approaches employed to correct the problem and mistakes that may result in significant losses for the organization.
So, when non-conformances have been discovered, the organization is able to understand the damage caused, the financial losses incurred and the reputation damage it caused. But with a better understanding of the rate of impact, the organization can also learn from mistakes and implement preventative actions that could safeguard it from the recurrence of the same problem in the future.
Promoting and facilitating better planning
Any organization requires a better understanding of the challenges it faces and knowing how to deal with them. Root Cause Analysis incentivizes the organization’s players to front and prioritizes the idea of better planning. This will help in deriving the best mechanisms for solving problems by effectively operationalizing quality management systems in the organization.
Eradicating unnecessary costs
Root Cause Analysis provides crucial information about the risks and costs that arise as a result of non-conformance. The organization will be able to understand the costs associated with the problem and how to mitigate them. For example, it could be crucial to understand the following;
- How much has been lost as a result of a non-conformance? This could be the number of revenues or profits that an organization lost as a setback after the problem occurred
- How much will the organization lose if the problem is ignored? When the problem is not effectively handled by ignoring it, it could result in more serious financial losses and other undesirable implications.
- How much does it take to solve the problem? The Root Cause Analysis must have this detail to help decision-makers within the organization because they need the right resources to execute the corrective action plan.
Improving workflow efficiency
Root Cause Analysis helps the organization identify the loopholes in its operations and close them. Such operational loopholes could be identified in form of deviation from the actual standard operating procedures, something that could lead to non-conformances in the organization. When established protocols and procedures are not followed by operational teams, it affects the efficiency and integrity of the entire workflow. Root Cause Analysis can help to;
- Emphasize the need for standardizing operational procedures and guidelines. Based on the findings and the investigations carried out, the organization will be forced to take both corrective and preventative actions by emphasizing the adoption of Standard operating procedures.
- Creating a sense of accountability where all players in the organization and the entire business chain live up to the established standards. Root Cause Analysis can expose loopholes in the workflow when there are no accountability mechanisms in place.
- Engaging teams to understand the problems they go through and collecting critical information in relation to why non-conformance happened. When employees share their experiences, the organization is able to act on their concerns as part of the overall strategy in trying to prevent the recurrence of the problem.
Establishing Quality Management Framework
A thorough investigation into the root causes of non-conformance, helps the organization reinvent its quality management systems and adopt a new operation philosophy. The organization can redesign its approach to quality assurance and risk assessment of its products and the entire ecosystem from manufacturing to the final consumer. Non-conformance is something that could undermine the delivery of quality products especially when proper procedures and guidelines aren’t followed. Therefore, strategic interventions like;
- Timely quality auditing and an inspection could be implemented. This basically means that the quality assurance department makes frequent evaluations of the Quality Management Systems to understand if they’re working as expected.
- Adopting standardized procedures by implementing the right framework for product quality assessment.
- Encouraging research and development where various studies are conducted to better understand how to adopt the right quality workflows within the organization.
Understanding the process of Root Cause Analysis
The process of executing Root Cause Analysis involves a couple of steps that have to be taken. These include the following:
Identify the problem
One of the primary goals of Root Cause Analysis is to identify the problem by gathering all the details that can help to explain why non-conformances happened. The root cause is identified and properly documented to help decision-makers in the organization understand the best mechanisms to employ while responding.
Gather data and document details
The best way to understand the problem is to have as many details as possible. The people charged with analyzing and studying the problem need to make sure every detail is gathered and nothing is left behind. Crucial questions like why did the problem happen? Who is responsible? How did it happen? When did it happen? And what should be done to offset the problem? In the process of gathering critical data about the problem, all these questions need to be answered in the most honest way. If any detail about the problem is left out, it could seriously limit the organization’s ability to execute an effective corrective action in response to the perceived non-conformances.
Solve the problem
When non-conformance is identified, the next step is to execute a corrective action plan to offset the problem. Usually, corrective actions could be a series of steps an organization can take while responding and mitigating the occurrence of non-conformances.
But also, while solving the problem, there are important considerations to put in mind and these include the following:
- Corrective actions should be implemented or executed based on the evidence proving the existence of the problem. If the organization and its decision-makers rely on inaccurate data, then the interventions they take are likely not to work regarding the identified problem.
- Understanding the actual costs involved. Root Cause Analysis as an entire process requires resources and a dedicated team to thoroughly study the problem and document all the details required. But also, the analysis needs to lay out the facts concerning the financial implications caused as a result of the problem.
- All important players should be involved. Throughout the execution of the Root Cause Analysis, all relevant parties should be consulted and take their input on the matter.
Pitfalls of the Root Cause Analysis process
As much as the Root Cause Analysis is a very essential process in quality management, there are certain pitfalls that could make it ineffective. These pitfalls include:
Relying on common knowledge or assumptions rather than evidence-based data: This usually happens when decision-makers do not want to invest in getting accurate information about the problem. Instead, they just want to quickly come up with a solution without having all the facts.
Not involving all stakeholders: While executing Root Cause Analysis, it’s important to involve all relevant parties. Failure to do this could lead to a situation where some ideas are not captured, and as a result, the organization might not be able to fully offset the problem.
Communication: After the Root Cause Analysis is concluded, it’s important to communicate the findings and decisions made to all stakeholders. This ensures everyone is on the same page and working together to solve the problem.
Not taking action: After the Root Cause Analysis is complete, and all the details about the problem have been gathered, it’s important to take action. But sometimes organizations might be reluctant to do this because of the fear of the unknown. Also, some decision-makers might not want to be held responsible for the actions taken.
Not tracking problems: In some cases, the Root Cause Analysis might identify a problem that happened in the past, and it’s no longer possible to take corrective action. In such a situation, it’s important to have traceability so that similar problems can be prevented in the future.
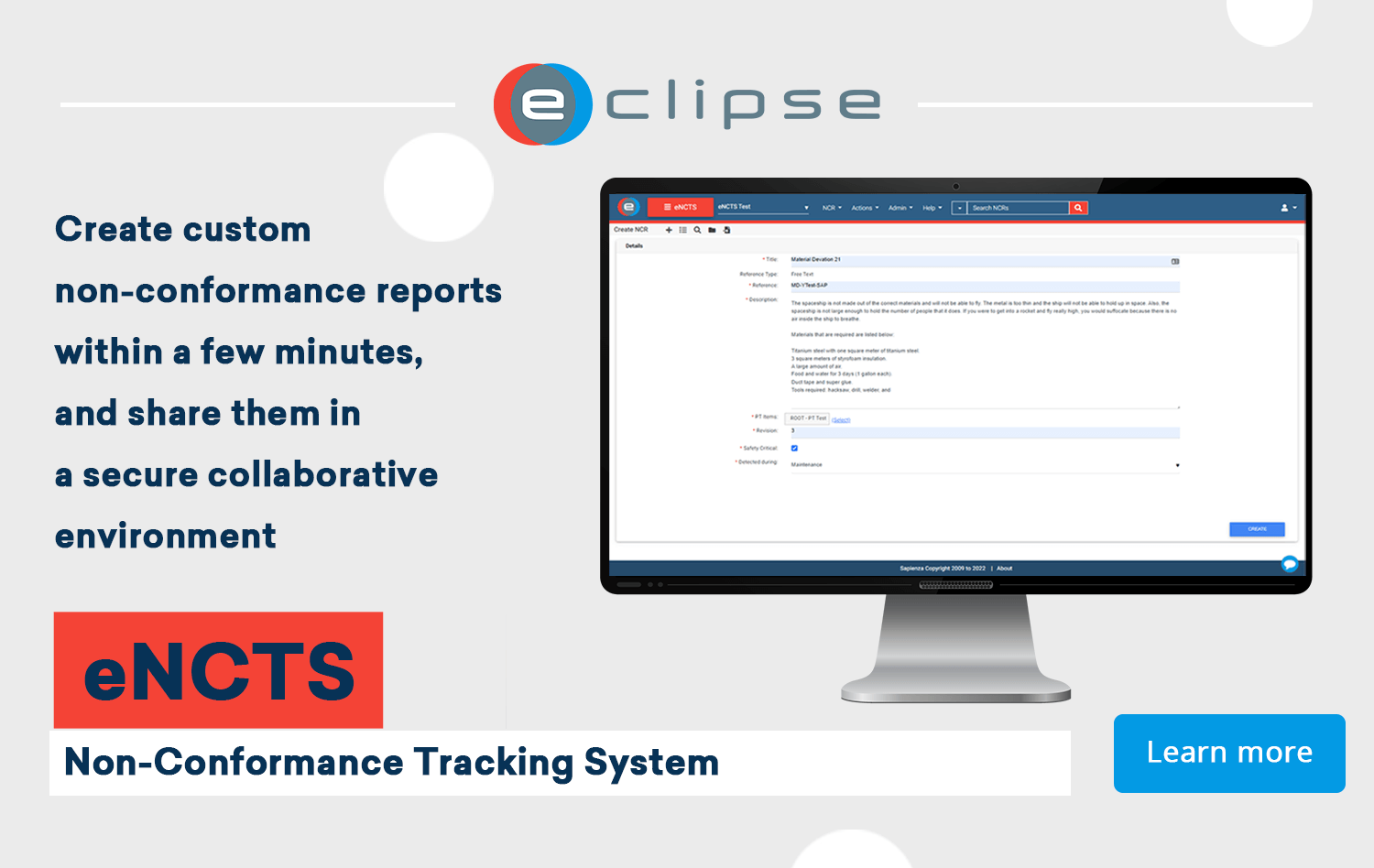
Use eNCTS during your Root Cause Analysis
The eNCTS Module and the ECLIPSE Software Suite help to prevent problems and pitfalls by providing an accurate way of capturing and recording non-conformances, actions and documents. It ensures that all stakeholders have access to the same information, and it’s possible to take corrective action quickly.
Contact our experts today to find out more about how you can use eNCTS and the ECLIPSE Software Suite in your organization.